Agricultural and Biological Research
RNI # 24/103/2012-R1
Research Article - (2023) Volume 39, Issue 2
Human-wildlife conflict is a contentious issue and crop damage by wild animals is one of the major problems in Darjeeling Hills. A study on human-wildlife conflict was conducted in seven villages in the hilly region of Darjeeling District, West Bengal, India, from April 2018 to March 2022 to assess the crop damage by wild animals and the economic loss incurred to the marginal farmers. The study indicated that crop damage by wild animals has increased significantly in recent years to such a great extent that the farmers have to abandon agriculture totally or change their agriculture practices as an adaptation to the conflict. The key reasons are decreasing natural habitat and expansion of tea gardens, and also the significant decline of the key predator of this region, the leopard that checks the population of wild herbivores. Replacement of agricultural crops by the cultivation of medicinal plant species, which are not raided by wildlife, is suggested as a mitigation measure.
Human-wildlife conflict; Crop damage; Predators; Cultivation of medicinal plant
Probably the most widespread and persistent form of human-wildlife conflict in the tropical region is crop damage by wild animals [1-5]. Such damage not only adversely impacts staple food grains (rice, wheat, maize, sorghum, and millet); but also causes havoc to non-grain food crops (potatoes, peanuts, vegetables, sugarcane, bananas, cassava, coconuts, and cocoa), and commercial crops (rubber, tea, coffee, and spices) [6,7]. In addition to the feeding of crops by animals, damage also results from trampling, rooting, and other forms of wastage. The proximity of wild animal habitats to agricultural farms has long been conceded to encourage human-wildlife conflict throughout the globe, with elephants, ungulates, and primates all responsible for creating problems for local farmers across Africa and Asia [8-11]. Large areas of natural habitats are being brought under human-managed systems for increasing productivity to fulfil the demand of the growing population, thus resulting in the fragmentation of wildlife habitats, which compel them to raid croplands causing severe damage [12,13]. The All India Network Project on Vertebrate Pest Management conducted studies over a decade that showed that the level of damage caused by different species of rodents was to the tune of 15%, followed by birds 9%. Recent studies also revealed that damage to different crops by the wild boar varies from 15%-40%, nilgai to the extent of 10%-30%, elephants, 20%-50%, rhesus macaque, 10%-30%, black buck, 5%-15% and gaur, 5%-10% [14]. The level and intensity of damage vary with the population density of wild animals, cropping pattern, the extent of cropland, season, and stage of the crop. The greater resilience and adaptability of wild animals to live successfully close to agricultural lands and human habitation chiefly because of reduced predatory pressure and regular availability of nutrientrich food (crops) round the year. As the relationships between humans and wildlife vary with geographical regions, there is no available perpetual solution for mitigating human-wildlife conflict. These can culminate in potential harm to all involved, and lead to negative human attitudes, with a decrease in human appreciation of wildlife and potentially severe detrimental effects on conservation [15]. In the Darjeeling district, West Bengal, India, less than 1.5% of the farmlands belong to marginal farmers [16] while the rest are occupied by different tea estates. In this district, the conservation discourse has a history of being shouldered by the Forest Department, with people’s participation still minimal or totally non-existent [17]. Participatory models of Joint Forest Management do not address key issues of ownership, decision-making spaces, participation and access, and benefit sharing [18], and within the limited mountain agricultural productivity and exploitative market, man-animal conflict takes a large toll on the local communities. A survey was conducted for the last four years indicates a steep rise in crop damage by the wild animals in the seven villages of Darjeeling hills causing a sharp decline in production. Decreasing natural habitat and expansion of tea estates drive the wild animals to raid crops in these areas more frequently, resulting in higher levels of damage. Now, crop raiding by wild animals in those villages has become a daily incidence, especially during the night. The crop damage by wild animals creates huge pressure on the livelihood of the local farmers that are often resulted in direct man-animal conflicts.
Study sites
The study was conducted from April 2018 to March 2022 in seven villages in the Darjeeling district, India (Figure 1). A total of 366 farmers were present in that study area. Major types of cultivated crops in those areas are Maize, potato, peas, squash, beans, and cabbage. The geographical locations, number of farmers, and altitude of the study areas are summarized in Table 1.
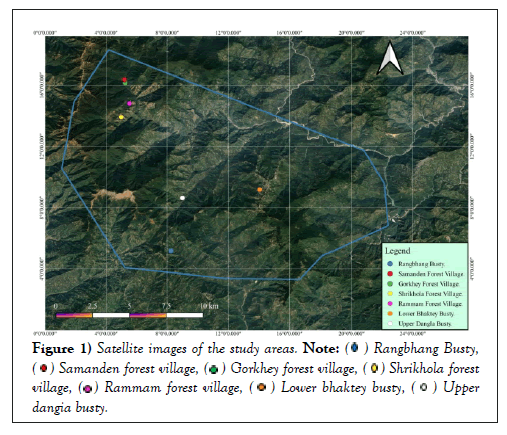
Figure 1: Satellite images of the study areas. 
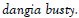
| Sl. No. | Name of the Village | Number of Farmers | Latitude (˚N) | Longitude (˚E) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gorkhey forest village | 38 | 27˚11′19″ | 88˚04′17″ | 2400 |
| 2 | Rammam forest village | 60 | 27˚09′21″ | 88˚04′56″ | 2300 |
| 3 | Samanden forest village | 35 | 27˚10′52″ | 88˚04′14″ | 2360 |
| 4 | Shrikhola forest village | 71 | 27˚04′46″ | 88˚03′46″ | 2357 |
| 5 | Upper dangia busty | 42 | 27˚01′34″ | 88˚09′14″ | 1238 |
| 6 | Lower bhaktey busty | 87 | 27˚02′21″ | 88˚15′05″ | 1739 |
| 7 | Rangbhang busty | 33 | 26˚57′11″ | 88˚08′05″ | 1612 |
Table 1: Geographical location, number of farmers and Altitude of the villages selected for the present study.
Trends in the crop damage by the wild animals
Trends in Crop Damage by wild animals were analysed from the time series of yearly crop damage (in percentage) trends using Poisson regression with the program TRIM [20]. The fit of the models was assessed using over dispersion, serial correlation and Wald χ² test. The overall trends in yearly indices were computed as summary statistics. Multiplicative slopes were used to express these trends [i.e, yearly multiplication factors (1=stable)] and the trends were classified according to statistical significance and magnitude:
a. Strong increase–increase significantly >5% per year and thus the lower limit of the confidence interval of the slope estimate is >1.05.
b. Moderate increase–a significant increase, but not significantly >5% per year; the lower limit of the confidence interval is >1.0 but <1.05.
Estimation of crop damage
Crop damage incidences were recorded from April 2018 to March 2022, and the species for crop damage was quantified. This was done by selecting all the farmers in each study area and conducting a questionnaire survey where information regarding the total agricultural land area, number and types of crops cultivated, wildlife species that invaded the agricultural area, duration, frequency, and amount of crop loss and economic loss caused to the farming households each year were inquired about [19]. The questionnaire also intended on the perception of farmers on humanwildlife conflict, and the mitigation measures practiced by them.
The economic loss was estimated by multiplying the quantity of crops damaged with the market value of the respective crops. The selling price of each crop was monitored in each village each year. The variances of crop damage during the study period were analysed using one-way Repeatedmeasures ANOVA (PAST. PAleontological STatistics, version 4.03) as the data were collected from seven villages in four consecutive years, using percentage data of crop damage.
The estimation of crop damages of different areas in four consecutive years as well as types of cultivated crops and causative wild animals for crop damage are summarized in Table 2. Among all study areas, the maximum crop damage in 2021-22 was recorded in Rammam forest village (95.66%, 3,728,300/-), followed by Shrikhola forest village (92%, 3,203,900/-), Gorkhey forest village (90%, Rs.1,434,000/-) Lower bhaktey busty (56.43%, Rs.96490/-), Upper dangia busty (51.27%, Rs.182390/-), Rangbhang busty (43.39% Rs. 85730/-), and Samanden forest village (40%, Rs.639,100/-). The model-based index values of Table 3 indicated that there is a strong increase in crop damage in Upper Dangia Busty and Gorkhey forest village; while a moderate increase was observed in Lower bhaktey busty and Rangbhang busty. The overall trends in these seven study areas also showed a strong increase in crop damage. The result of one-way Repeated-measures ANOVA also showed significant temporal variation (F=5.17; P=0.042) in crop damage during the last four years (Table 4).
| Area | Damage of crops in three consecutive years | Types of cultivated crops | Major causative animals | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2021-22 | |||
| Upper dangia busty | 39.88% Rs.118,500/- | 40% Rs.161,000/- | 47.71% Rs.168,800/- | 51.27% Rs.182,390/- | Maize, potato, peas, beans, cardamom, paddy | Assamese Macaque, Orange-Bellied Himalayan Squirrel, Wild Boar, Himalayan Porcupine. |
| Lower bhaktey busty | 52.5% Rs. 86500/- |
55% Rs. 85500/- |
55.08% Rs. 93500/- | 56.43% Rs.96490/- | Maize, pumpkin, beans, squash, cauliflower, leafy greens | Assamese Macaque, Orange-Bellied Himalayan Squirrel, Wild Boar, Himalayan Porcupine, Kalij Pheasant |
| Rangbhang busty | 38.85% Rs. 72380/- |
37.95% Rs. 73920/- |
41.65% Rs. 81700/- |
43.39% Rs.85730/- |
Maize, potato, pea, squash, beans, cardamom, cabbage, carrot, ginger | Wild Boar, Kalij Pheasant, Himalayan Porcupine, Barking Deer |
| Gorkhey forest village | 22.5% Rs.284,400/- | 26.66% Rs.361,200/- | 27.5% Rs.374,400/- | 90% Rs.1,434,000/- | Maize, potato, peas, squash, beans and cabbage | Wild boar, Himalayan Black Bear, Himalayan Porcupine, Barking Deer, Kalij Pheasant, Orange- Bellied Himalayan Squirrel. |
| Rammam forest village | 31% Rs.1,210,200/- | 34.86% Rs.1,598,000/- | 32.66% Rs.1,592,100/- | 95.66% Rs.3,728,300/- | Maize, potato, peas, squash, beans and cabbage | Wild boar, Himalayan Black Bear, Himalayan Porcupine, Barking Deer, Kalij Pheasant, Orange- Bellied Himalayan Squirrel. |
| Samanden forest village | 32.5% Rs.510,400/- | 35% Rs.556,600/- | 25.83% Rs.455,400/- | 40% Rs.639,100/- | Maize, potato, peas, squash, beans and cabbage | Wild boar, Himalayan Black Bear, Himalayan Porcupine, Barking Deer, Kalij Pheasant, Orange- Bellied Himalayan Squirrel. |
| Shrikhola forest village | 22.5% Rs.729,100/- | 22.5% Rs.692,300/- | 22.83% Rs.768,200/- | 92% Rs.3,203,900/- | Maize, potato, peas, squash, beans and cabbage | Wild boar, Himalayan Black Bear, Himalayan Porcupine, Barking Deer, Kalij Pheasant, Orange- Bellied Himalayan Squirrel. |
Table 2: Estimation of crop damage (in Percentage and Indian Rupee (Rs.)) of the study areas in four consecutive years.
| Village name | Indexa | Estimate SEb | Wald χ2 (df = 1)c | P | Inferenced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper dangia busty | 1.351 | 0.093 ± 0.018 | 32.95 | <0.001 | Strong increase |
| Lower bhaktey busty | 1.062 | 0.022 ± 0.005 | 16.77 | <0.001 | Moderate increase |
| Rangbhang busty | 1.148 | 0.042 ± 0.013 | 12.65 | <0.001 | Moderate increase |
| Gorkhey forest village | 4.597 | 0.419 ± 0.155 | 8.33 | 0.004 | Strong increase |
| Rammam forest village | 3.299 | 0.331 ± 0.145 | 5.85 | 0.016 | Uncertain |
| Samanden forest village | 1.07 | 0.032 ± 0.075 | 0.08 | 0.771 | Uncertain |
| Shrikhola forest village | 5.25 | 0.424 ± 0.191 | 5.81 | 0.016 | Uncertain |
| Overall trend | 1.975 | 0.202 ± 0.059 | 12.49 | <0.001 | Strong increase |
Note: aModel-based indices, calculated from the summation of model predictions of all time points from 2018 to 2022 (n=4) i.e, the model-based time totals; the index for 2018 is 1.00; bSlope parameter estimate; cWald-test for significance of slope parameter; dModel-based inference.
Table 3: Poisson-based Log-linear models for the trends of crop damage in seven villages at Darjeeling Hills between 2018 and 2022.
| Year | Sum of squares | df | Mean square | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between years 2021-2022 |
5221.9 | 3 | 1741 | 6.65 | 0.003 |
| Between sites | 1127.7 | 187.9 | 0.72 | 0.641 |
Table 4: One-way repeated measures ANOVA showing temporal and spatial variation in crop damage.
Although the causative animals responsible for crop damage are wild pig (Sus scrofa), Himalayan crestless porcupine (Hystrix hodgsoni), barking deer (Muntiacus muntjak), Assamese macaque (Macaca assamensis), himalayan black bear (Ursus thibetanus) and a number of birds. But Wild boar (Sus scrofa) alone causes nearly ninety percent of the total damage.
In recent years Crop damage by wild animals has gone beyond the nominal loss to the farmers having to abandon agriculture totally or change their agriculture practices as an adaptation to the conflict. Today, this is not only restricted to the forest fringe communities but also is spreading out to villages adjacent to urban enclaves like Lower Bhaktey Busty which is adjacent to Darjeeling Town. And wild boar is the major element for crop destruction in this region as in many other parts of the world [21]. The issue has become a critical point of discussion and became a focal point of community conversations in this part of the Himalayas, yet it still remains being discussed locally and has not got any significant ground of power and policies. Chiefly because the human-wildlife conflict discourse is currently mega-fauna and plains-centric. Mountain human-wildlife conflict is the result of a complex myriad of primarily small mammals raiding crops and livestock that do not stand the same graces as the prima donna megafauna of conservation or are not listed as problem animals of human-wildlife conflict [17]. The limited space for people’s participation has meant that a core community issue has not gained prominence as much as it should have in policy debates. This gets compounded with the fact that the focus is on the region’s investment in conservation for national and global goods which is not always sensitive to micro-local needs. Forest villagers are a minuscule percentage of the population and extremely marginalized, making their voices difficult to climb the ladder of voices that are heard.
High levels of crop damage by wild animals as noticed in the study villages are chiefly because of decreasing natural habitat and expansion of tea estates that drive the wild animals to raid crops in these areas more frequently, resulting in a higher level of damage. Due to the lack of natural vegetation cover, leopards are also very less frequent in those areas. Usually, people have a negative attitude towards all wild animals in this area, especially the leopards that sometimes lift their livestock. But recently they are slowly realizing the importance of large predators like leopards for the protection of their crops.
Damage to crops resulted in a serious negative impact on wildlife management by the local communities due to their smaller holdings, geographic marginality, and lack of off-farm income-generating options, often forcing them to illicit poaching of wildlife. So, there is an urgent need of implementing mitigation plans to ensure the goal of biodiversity conservation along with the sustainable livelihood of local communities. The cultivation of medicinal plants having good market value, and are not raided by wildlife, could be encouraged to avoid economic losses.
Developing and implementing management interventions are urgently needed that address the goal of biodiversity conservation together with the sustainable livelihood of local communities. Replacing the cultivation of agricultural crops with economically important medicinal plant species (e.g., Castor (Ricinus communis), Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius)), which are not raided by wild animals, could be an option to discourage wildlife from raiding crop fields and avoiding the economic losses to the local communities. It was also advised to the local farmers to plant castor in four thick rows around the crops that can deter wild animals like wild boar and deer from raiding crops.
I deeply acknowledge my gratitude to Shuvam Sharma, Susadhna Gurung and Palden Tamang for their immense support during the entire field study. I also gratefully acknowledge the active cooperation of the farmers of the study area for their active cooperation during the entire study period.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [Pub Med]
Citation: Hazra P. Trends of crop damage by wild animals in Darjeeling Hills, West Bengal, India. AGBIR.2023; 39(2):482-486.
Received: 04-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. AGBIR-23-88658; , Pre QC No. AGBIR-23-88658 (PQ); Editor assigned: 07-Feb-2023, Pre QC No. AGBIR-23-88658 (PQ); Reviewed: 21-Feb-2023, QC No. AGBIR-23-88658; Revised: 28-Feb-2023, Manuscript No. AGBIR-23-88658 (R); Published: 07-Mar-2023, DOI: 10.35248/0970-1907.23.39.482-486
Copyright: This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@pulsus.com This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
